VET APPROVED

The information is current and up-to-date in accordance with the latest veterinarian research.
Learn more »Click to Skip Ahead
If you are the proud parent of a bearded dragon, you may have wondered about the reproductive habits of these unique pets. Understanding how bearded dragons mate isn’t just a fascinating insight into their biology—it can also help you provide the best care for your scaly friend. So, let’s learn more about this interesting topic!

Understanding the Bearded Dragon Life Cycle
Before we delve into their mating rituals, let’s first understand the lifecycle of a bearded dragon. Bearded dragons, known scientifically as Pogona vitticeps, typically reach sexual maturity between 12 and 18 months, depending on their individual health, nutrition, and care, with males often maturing slightly earlier than females.
Unlike mammals, bearded dragons exhibit clear but subtle sexual dimorphism, which means it can be challenging to determine their gender without experience. However, as they approach maturity, there are reliable physical traits you can observe.
Male bearded dragons tend to have larger heads, larger femoral pores, and wider tails than females. They also have two visible bulges at the base of the tail, which are part of their reproductive organs. Females, on the other hand, often have a rounder body, especially during the breeding season or when carrying eggs.
The Mating Process
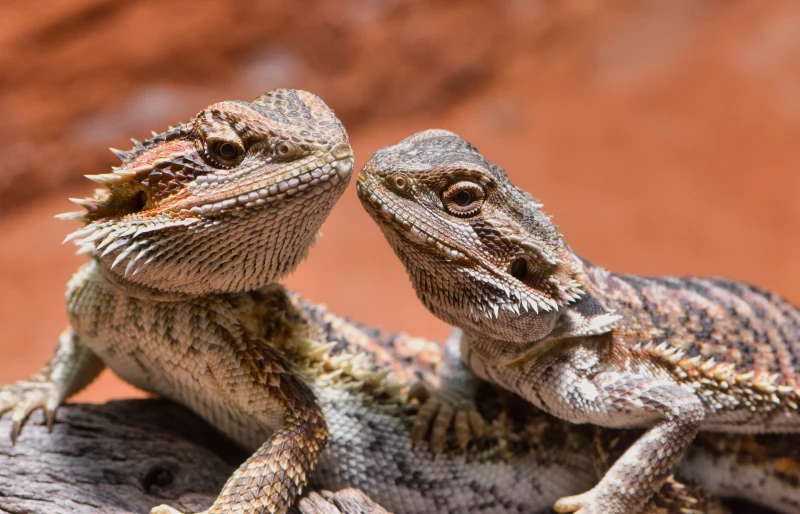

Once a male and female bearded dragon reach sexual maturity, nature takes its course. The male bearded dragon initiates the mating process, often displaying courtship behaviors that are fascinating to observe.
These may include bobbing their head rapidly, stamping their feet, or flaunting their beard, which darkens and puffs up as a sign of dominance and attraction.
The female, on the other hand, may show passive submission by raising one of her front legs or may play hard to get, running away from the male. If she is receptive, the male will climb onto the female’s back, biting her neck firmly but briefly as he aligns their cloaca for mating.
It’s important to note that bearded dragon mating can seem aggressive, but it’s part of their natural behavior. However, persistent chasing, repeated biting, or the inability of the female to escape may cause stress or injury, so close supervision and separation when necessary are essential.
After Mating: The Egg-Laying Process
Following successful mating, a female bearded dragon will usually lay a clutch of eggs—typically 15 to 30—about four to six weeks later. During this time, she may display nesting behaviors, such as digging or appearing restless.
Ensure she has a suitable, safe place for egg-laying, such as a nesting box filled with moist sand or soil mixture that holds its shape when compressed, allowing her to dig a stable tunnel.

Caring for Your Bearded Dragons During Breeding

Taking care of your bearded dragons during breeding is paramount. Ensure they have a balanced diet rich in calcium, with appropriate calcium-to-phosphorus ratios and vitamin D3 support, which is essential for females producing eggs. Also, maintaining a warm and comfortable environment is crucial.
Bearded dragons are native to the arid regions of Australia, so their habitat should mimic this, with a basking area that reaches about 100–110°F (37–43°C).
Furthermore, maintain a close watch on the female bearded dragon after egg-laying. This process can drain her energy and nutrients, so increased hydration, continued calcium supplementation, and veterinary monitoring for complications such as egg binding are recommended.
Breeding Bearded Dragons Responsibly
While breeding bearded dragons can be an exciting prospect, it’s essential to remember the responsibility that comes with it. The pet trade is already saturated with bearded dragons, so consider the welfare of potential offspring and their demand before allowing your pets to breed.
Keeping your bearded dragons healthy and safe during the mating process is a matter of careful observation, appropriate preparation, and committed aftercare. Always consult with a veterinarian experienced in exotic pets to ensure you’re providing the best care for your scaly friends, especially during this crucial time.
Keeping Your Bearded Dragon Happy and Healthy

Beyond understanding their mating rituals, it’s essential to ensure that your bearded dragon is always in top condition, both physically and mentally.
Physical Health
Proper nutrition is the cornerstone of physical health. Ensure a balanced diet of appropriately sized insects such as crickets, dubia roaches, or black soldier fly larvae, and leafy greens, with fruits offered sparingly, if at all, due to their sugar content. Mealworms should be limited because of their high chitin and fat content. Regular vet check-ups will help prevent any potential health problems. Pay attention to their behavior—any changes could be a sign of stress or illness.
Mental Health
Just like any other pet, bearded dragons need mental stimulation. Encourage natural behaviors by providing climbing branches, basking platforms, and hiding spots. Interaction is also important. Handle your bearded dragon gently and frequently to help them get used to human contact.
Suitable Habitat
A suitable environment contributes significantly to your bearded dragon’s happiness and health. Create a warm gradient in their enclosure, with a cooler zone (approximately 75–85°F / 24–29°C) and a dedicated heated basking spot reaching 100–110°F (38–43°C). UVB light is essential for them to synthesize vitamin D3 and metabolize calcium. Remember that UVB lights need to be replaced on a scheduled basis to ensure effective UVB output, even if the bulb still produces visible light. Regularly clean the enclosure to prevent pathogenic bacterial buildup and reduce the risk of infectious disease.
Social Interaction
Since bearded dragons are not pack animals, cohabitation is generally discouraged, particularly for adults. Even females may compete for resources, and housing two males together should always be avoided due to territorial aggression.

Happy, Healthy Dragons
Remember, a happy bearded dragon is an active one. Regular interaction, a stimulating environment, a balanced diet, and proper care during mating and breeding will ensure your scaly friend lives a long, healthy, and content life.

Final Thoughts
Understanding how bearded dragons mate allows us to appreciate the fascinating intricacies of their biology. More importantly, it equips us to take better care of our unique pets. So while the mating process may seem a little unusual to human observers, it’s simply a testament to the marvel of nature.
Featured Image Credit: Zh.anna, Shutterstock
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate (you can leave written feedback after clicking submit)
Help us improve Hepper for pet parents!
Your feedback really matters.
What did you like about this post? Also how can we improve it?